Warehouse management knowledge collection
Learn these flow charts and tables well, and warehouse management will no longer be a problem!
1. What are the general principles for material storage and maintenance?
(1) The warehousing department should divide the warehousing area into raw materials, semi-finished products, finished products and defective products according to the nature of the inventory to facilitate management.
(2) Plan the products into different areas at the job site according to the production process, as labels for the temporary storage management of the products in each production line.
(3) The following four items should be considered as basic principles of storage design to facilitate the reception and distribution work.
① Liquidity:
Frequently used items should be stored close to the receiving and insertion areas to reduce the transportation cost of workers’ round-trip time.
② Similarity:
Items that are often used together should be placed in the same area to shorten time.
③ Item size:
When designing storage, the storage location should be given appropriate storage space according to the size of the items to be stored to ensure that the space can be fully utilized.
④ Security
Safety should be the first priority in the storage of items. For example, when storing dangerous items, some safety measures should be taken into consideration to maintain the safety of the warehouse and factory area.
(4) Each material must have a fixed storage location, and the materials should be placed according to the storage location. The warehousing department should regularly check whether the storage location of the inventory is correct. If there is an error, the cause should be found out, and attention should be paid to preventing the error situation. Happen again.
2. What are the general principles for material handling operations?
When handling materials, appropriate tools or other methods must be selected based on the actual situation, such as the size, quantity, and stacking height of the materials, and the following principles must be followed:
(1) When handling, keep the passage clear, pay attention to safety and adopt appropriate handling methods.
(2) Use appropriate handling methods and handling tools depending on the size of the items being moved. Such as hydraulic trucks, trolleys or forklifts, etc.
(3) Components and fragile items should avoid collision when being transported, and pay attention to moisture-proof and anti-fouling to ensure their precision. They must be handled with care when placed.
3. What matters should be paid attention to when storing materials?
If there are no special requirements for the storage of materials, appropriate and effective storage methods should be adopted according to the size, height, weight, etc. of the materials. The general standards are as follows:
(1)Height:
The total stacking height is generally limited to less than 3 meters, and when placing racks, each layer should not exceed 1.5 meters.
(2) Weight:
When placing materials, the weight of the materials should be considered. Heaviest materials should be placed on the lower floor as much as possible to avoid accidents when accessing materials.
(3) Storage regulations for integrated circuits (ICs) and fragile items:
①Integrated circuits should be stored in original packaging or in anti-static containers to prevent damage to quality caused by static electricity or other reasons.
② When integrated circuits are shipped out of the warehouse or in inventory due to need, they must be placed in anti-static containers to prevent bending and damage of IC pins due to careless storage. Anti-static tools must be used when moving integrated circuits. When moving (such as vacuum pens), try to avoid using your hands.
③Fragile items should be placed on the lower shelf of the material rack or packed in boxes to ensure safety.
④The above materials must be worked on the workbench when sending/receiving them.
(4) Materials with expiration dates must be specially marked.
(5) During the storage process, if the product is dropped or if quality problems are suspected, the quality must be re-confirmed with the quality control personnel.
(6) When storing materials, pay attention to the surrounding environment control. Changes in temperature and humidity need to be recorded in the “Temperature Record Form”. Because electronic parts are easily oxidized and damaged in an environment with too high humidity, they must be There are some protective measures such as dehumidifiers and other equipment to reduce humidity to avoid material damage and losses.
4. How many areas is the receiving area generally divided into?
(1) Incoming material inspection area
After receiving the materials, the receiving personnel of the warehousing department will place the materials in this area, and different materials must be placed separately and cannot be mixed together.
(2) Feed qualified area
Materials that have passed the inspection by the quality control department are placed in this area, waiting for the warehouse receiving personnel to enter the warehouse.
(3) Inspection and return area
Materials that fail quality control inspection are placed in this area, waiting for processing by the supplier.
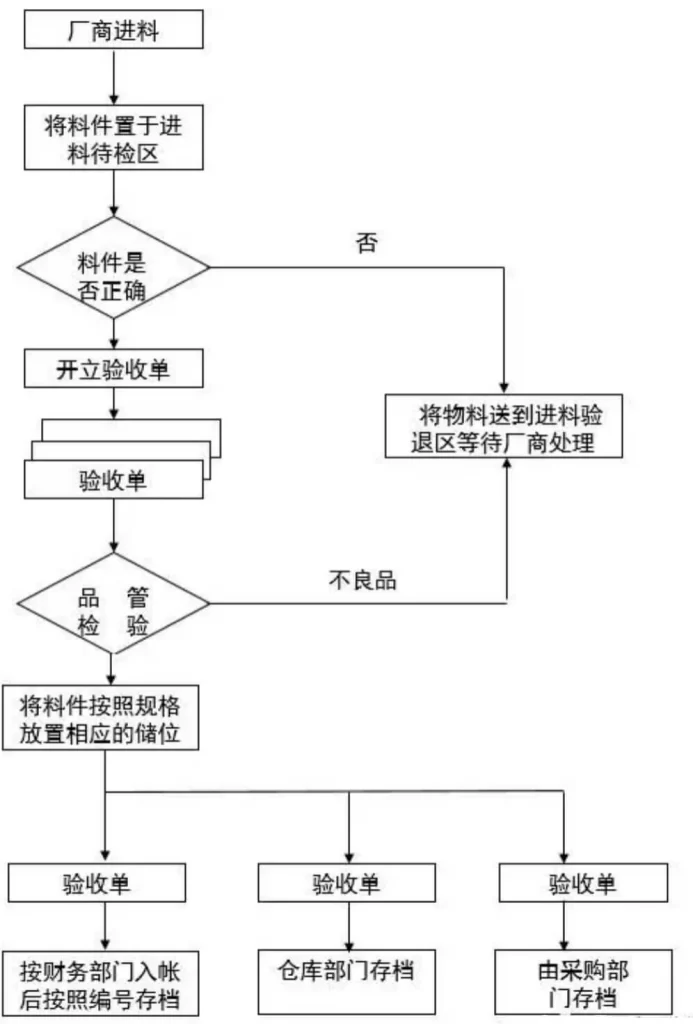
5. How to complete the receiving, feeding and warehousing operations?
(1) Other storage departments must have a specific receiving area to temporarily store materials imported from manufacturers, waiting for inspection and storage. They must not be placed randomly.
(2) After receiving the materials from the freight company’s delivery personnel or manufacturers, the warehousing personnel place the materials in the area to be inspected, and then check the name, specification, material number, and quantity of the received materials according to the information provided by the production management department , issue an “Acceptance Form” after it is correct, and submit it to the quality control department to inspect the materials on time. If the materials delivered do not match the information provided by the competent department, the materials will be placed in the incoming material inspection and return area, waiting for the manufacturer deal with.
(3) Warehousing department personnel shall follow the material acceptance form that has passed the inspection by the quality control department. Place the material in a fixed storage location. Before placing the material, the material’s box or box must be marked with the date of delivery, and the date of delivery, receipt number, quantity, etc. must be noted on the material inventory card. information for future tracking.
(4) The “Acceptance Form” is in triplicate, as follows:
The first and second copies: Send them to the financial department for recording and then file them according to the number.
Third page: The warehousing department registers the materials and files them according to the number.
The fourth page: Submit it to the Purchasing Department for archiving.
6. Feeding operation flow chart
7. How does the warehouse deliver materials?
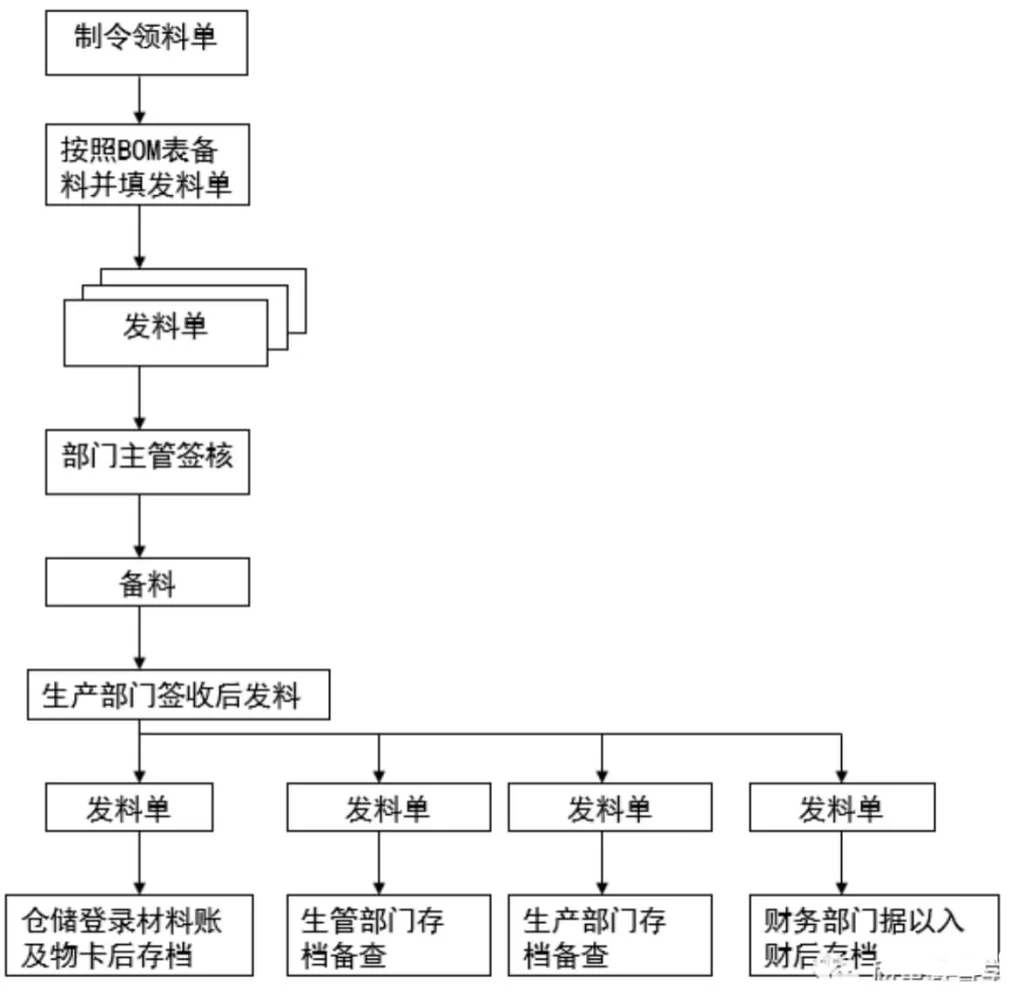
(1) After the warehousing department prepares materials according to the “Manufacturing Order Requisition List” issued by the production management department (provided by the production management department), the materials should be prepared according to the BOM list. During the material preparation process, the movement of materials must comply with the handling rules. After the materials are prepared, a “Material Distribution Sheet” must be prepared and issued. After being signed by the supervisor, it will be sent to the production department and notified of the material requisition.
(2) Materials must be distributed on a first-in, first-out basis to maintain the applicability of the materials.
(3) When preparing materials, the material preparation personnel must place the prepared materials in a fixed area (such as the material preparation area) and must not place them randomly; materials from different batches must be placed separately and cannot be mixed together; and each batch of materials must be placed separately. Batch materials must be marked with the name, specifications, order number, and batch size to avoid mishandling or other errors.
(4) After receiving the invoice issued by the warehousing department, the production department will go to the warehouse to pick up the materials according to the invoice. When the production department is picking up materials, warehouse stocking personnel must be there to assist. If there are errors or discrepancies in material names, specifications, quantities, etc., the problem can be solved immediately.
(5) Important parts (such as IC), etc., may need to use materials that are different from those listed in the BOM due to insufficient quantity. They must have documents recognized by the company to prove their use before they can be substituted. Otherwise, materials will not be issued.
(6) When issuing materials, warehousing personnel should indicate the remaining materials on the material control card and check whether the account materials are consistent. If there are any discrepancies, they must immediately check where the problem occurred and correct the error. Prevent similar errors from happening again next time.
(7) After the production department personnel have counted the materials according to the material issue list, they will sign and date the materials on the material issue list and then receive the materials back.
(8) The bill of materials usually consists of four or three copies. After the material is issued, it will be distributed by the warehousing department as follows:
The first copy: Send it to the financial department for accounting and then file it according to the number;
Second page: After the warehousing department logs in to the material account, it is archived in the order of numbers along with the “Material Requisition List” for future reference;
The third copy: Submit it together with the materials to the production department;
The fourth page: archived by the production management department for future reference.
8. Material issuing operation flow chart
9. How to return materials in the warehouse?
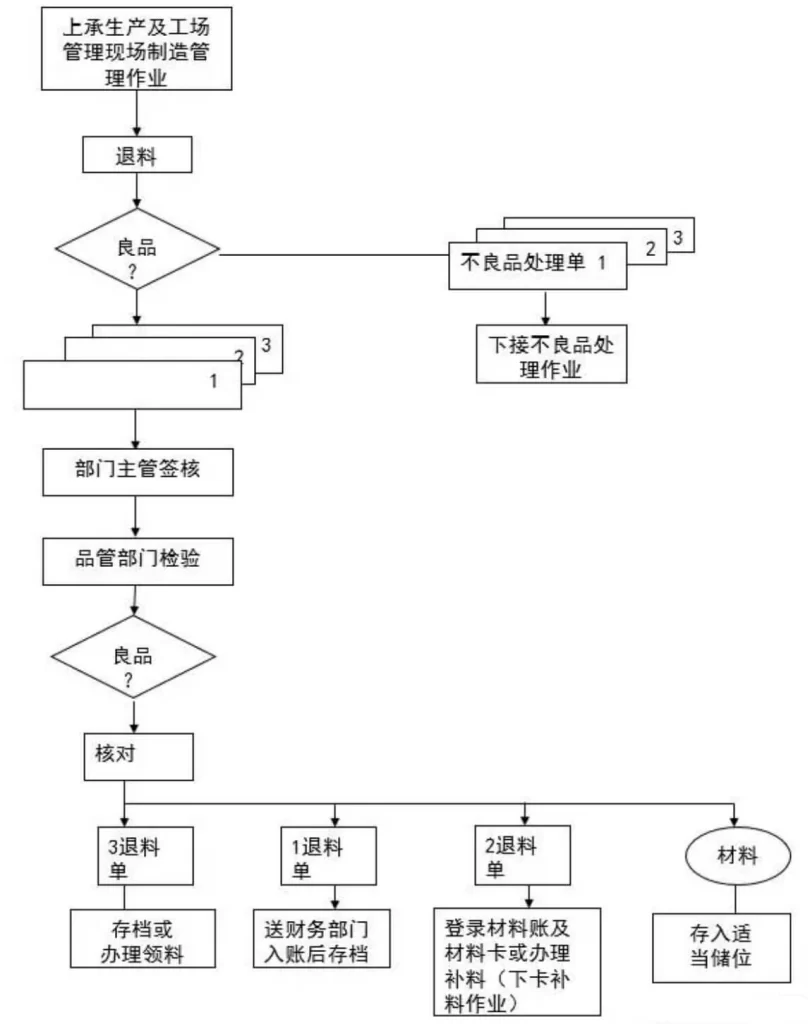
(1) When the production department must return materials due to engineering reasons, remaining materials at the end of the work order, packaging changes, etc., it should fill in the “Return Material Form”, which must indicate the date, returning department, and manufacturing work order number (production work order number). Order picking order number), machine model name, specifications, reason for returning materials, material number, department, quantity to be returned, etc., will be notified to the quality control department for inspection after approval by the department supervisor.
(2) The quality control department shall conduct inspections in accordance with the provisions of the “Quality Specifications” and endorse the inspection results in the “Quality Control Inspection” column of the return form. If any product is inspected as defective, return it to the production department, fill in a “Defective Product Processing Form” and handle the return according to the “Defective Product Processing Operation”; if it is a good product, notify the production department to handle the warehousing matters.
(3) The warehousing department receives the returned materials and return forms that have been inspected by quality control. After checking them, they fill in the actual return amount on the return form and store the materials in the appropriate storage location. The return form is in triplicate and divided into three parts. Send as follows:
The first page: Send it to the financial department for recording and then file it according to the number;
Second page: The warehousing department logs in to the material account or handles replenishment of materials; for details of subsequent operations, see “Replenishment Operations”;
The third copy: Send it to the production department for archiving and reference or for material collection.
10. How does the warehouse handle defective products?
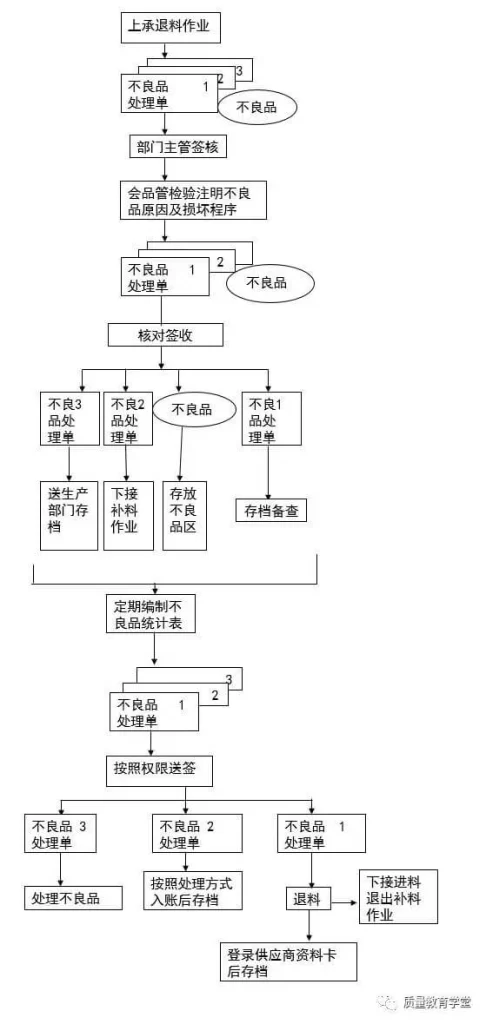
(1) When defective products are returned in the production department, the “Defective Product Disposal Form” should be filled in. After being signed by the department supervisor, the quality control department will inspect and indicate the cause of the defect, the extent of damage and the proposed treatment method, and send the defective products together with Submit it to the warehousing department.
(2) After the warehousing department receives the defective products and the defective product handling form that have been inspected by quality control and verify that they are correct, they place the defective products in the defective product area. The defective product handling form is in triplicate, as follows: The first page: Send to finance The department should archive it for future reference; the second page: the warehousing department should archive it for future reference; the third page: send it to the production department for archival purposes or to use it for material collection.
(3) The warehousing department should prepare a “Defective Product Statistics Table” every month in accordance with the “Defective Product Disposal Sheet”, indicating the number, date, item name and specification, quantity, and defective product handling order number. If the original is defective, the purchasing department should be notified to sign a claim or exchange.
(4) The defective product statistical form is in triplicate, and will be distributed as follows after approval: The first copy: sent to the purchasing department; the second copy: sent to the financial department according to the processing method and filed after the money is collected; the third copy: filed by the warehousing department for future reference , based on which defective products are dealt with.
11. Material return operation flow chart
12. Defective product processing operation flow chart
13. How to replenish materials in the warehouse?
(1) Material replenishment is applicable when there is a shortage of materials due to material returns from the production department or abnormal conditions in operations or equipment.
(2) When the production department is short of materials due to abnormal operation or equipment, it should fill in the “Material Requisition Form”, indicating the order number, date, application department, manufacturing work order number, product history specifications, material number, department, application quantity, Explain the reason for the application and send it to the department manager for approval before going to the warehouse to pick up the materials.
(3) After the warehousing department receives the “Material Picking List” and the “Material Return List” or “Defective Product Disposal Sheet” and they are correct, they will send the materials to the department supervisor for approval and then fill in the actual quantity shipped on the picking list. The “Material Picking List” is in triplicate, as follows: The first copy: sent to the financial department for archiving for future reference; the second copy: sent to the warehousing department for the purpose of issuing materials; the third copy: filed by the application department for future reference.
14. Material replenishment operation flow chart
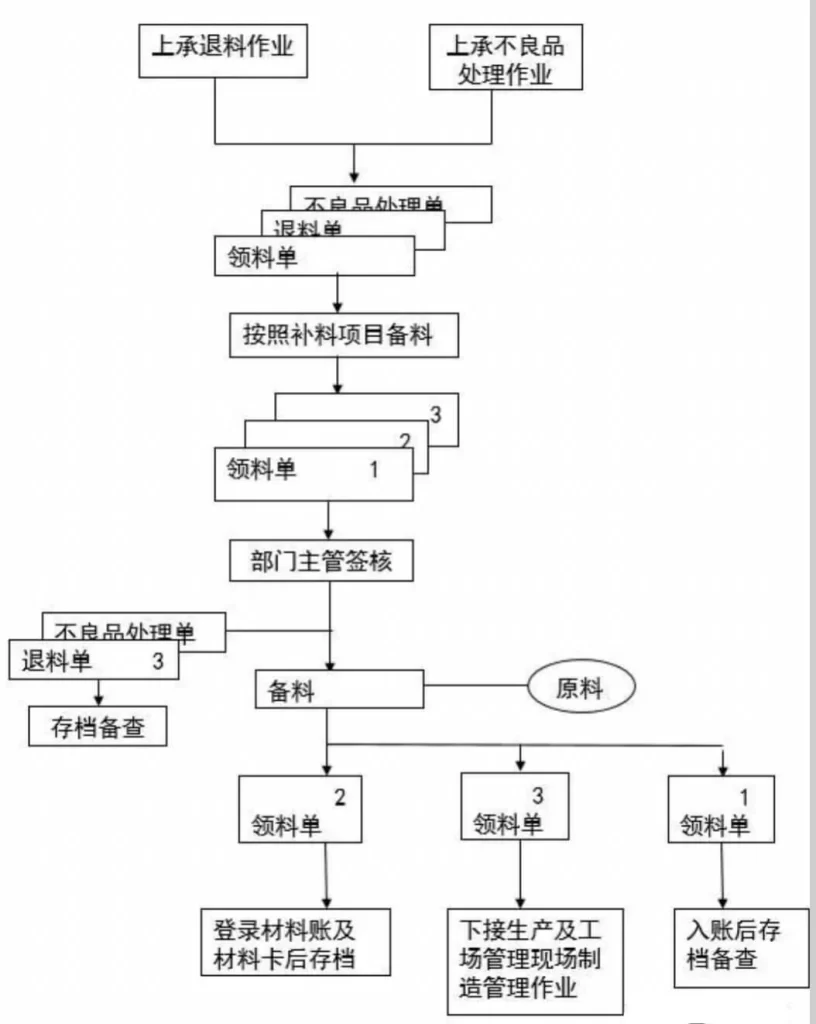
15. Production product warehousing operation process
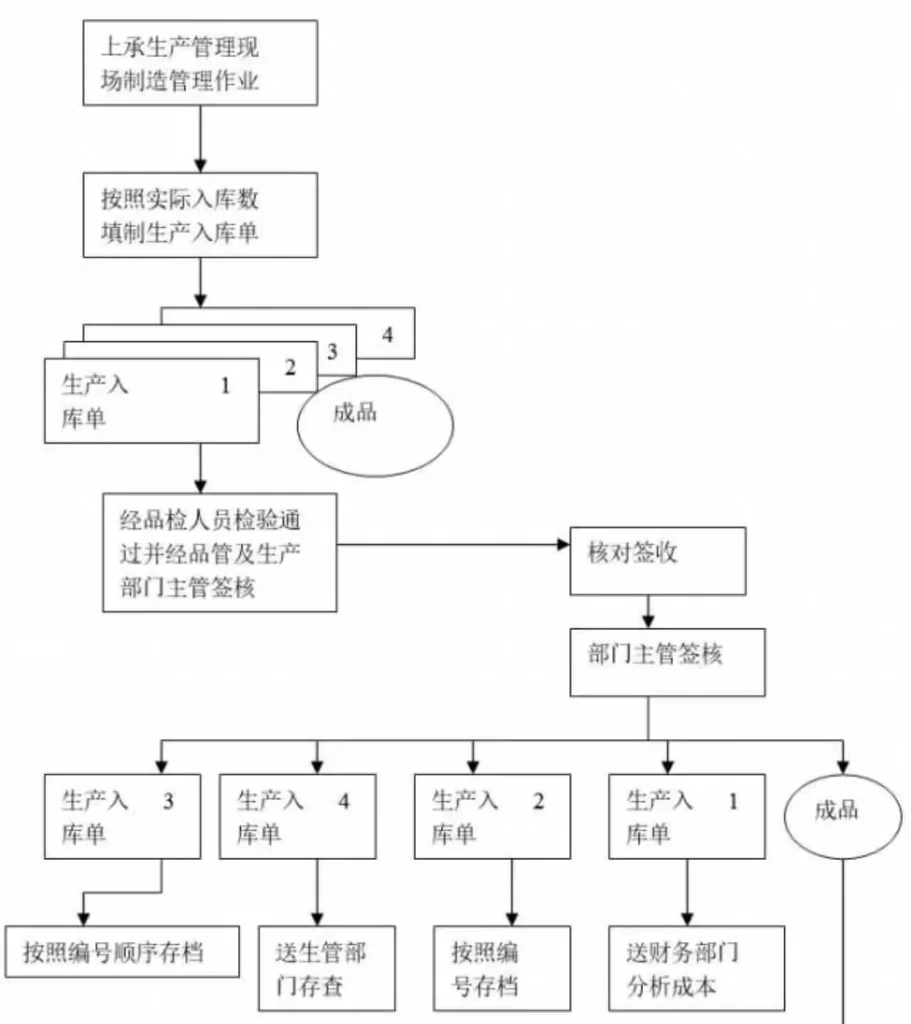
16. How to conduct inventory in the warehouse?
(1) This project is suitable for daily inventory operations of raw materials, work-in-progress, semi-finished products and finished products.
① In addition to the annual inventory twice a year, the raw materials, work-in-process, semi-finished products and finished products of each department should be randomly inspected and regularly checked every month according to the categories of raw materials, work-in-progress, semi-finished products and finished products.
② The warehousing department should conduct regular inventory inventory on its own every month, and the audit department should send personnel to conduct random inspections at any time.
③ When materials are randomly inspected and inventoried, the materials that are randomly inspected or inventoried will stop receiving and receiving materials. Material custodians are not allowed to leave their jobs without authorization when handling materials for random inspection or inventory, and must be properly prepared. , Assist in inventory.
④ If inventory materials and parts are found to be inconsistent after random inspection or inventory, and there are no special reasons, they will be handled according to the inventory adjustment method.
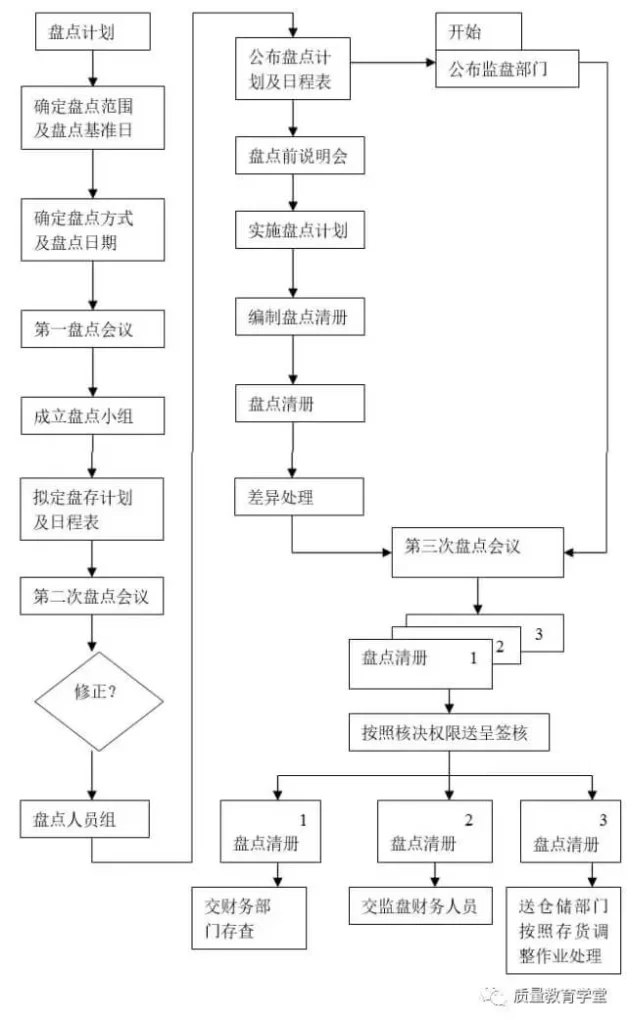
(2) The company should conduct a comprehensive inventory inventory at least once a year.
①The audit department should convene the first inventory meeting after determining the inventory scope, inventory basis, inventory method, inventory date and other relevant information before the inventory.
② Set up an inventory team and formulate an inventory plan and schedule.
③The proposed inventory plan and schedule should be determined by the second inventory meeting as the basis for organizing the inventory personnel.
④ The audit department shall notify the inventory supervision department of the determined inventory plan and schedule.
⑤ The audit department should hold an inventory briefing meeting to explain the inventory precautions in detail before the inventory.
⑥The financial department prepares an “inventory inventory” based on the inventory results, and the audit department holds a third inventory meeting to deal with the differences and submits an inventory report.
⑦The inventory list shall be made in triplicate and distributed as follows:
a. Submit one copy to the finance department for review:
b. A copy of the delivery record to be kept by the financial personnel for review;
c. Submit one copy to the warehousing department for processing according to the inventory adjustment operation.
17. Example of recording method for material inventory in a factory
The inventory of material warehouse is relatively simple due to the small object and scope.
(1) Inventory day
In principle, it is 4 hours in the afternoon at the end of each month. During the inventory period, items in the material warehouse are prohibited from moving, that is, they cannot be put in or out of the warehouse.
(2) Inventory personnel:
① Inventory: The warehouse management personnel of each project will inventory the materials in their respective charge.
② Inspection: Other material management personnel shall inspect the counting tickets of the inventory personnel.
③Count votes
a. It is made of two copies, one copy should be kept by the person taking inventory, and the other should be hung (sticked) on the items to be counted.
b. The inventory tickets are serially numbered so that they can be easily organized on the inventory list and will not be missed.
c. The counting tickets can be divided into three colors:
White – good quality
Yellow—sluggish product
Red—waste
④Inventory table
Classify the counting tickets into white, yellow, and red tickets, and transfer them to the counting table according to the consecutive numbers.
Inventory table in triplicate:
finance
Material control
Warehouse self-storage
Inspection personnel conduct random inspections according to the inventory list and inventory tickets.
18. Inventory operation flow chart
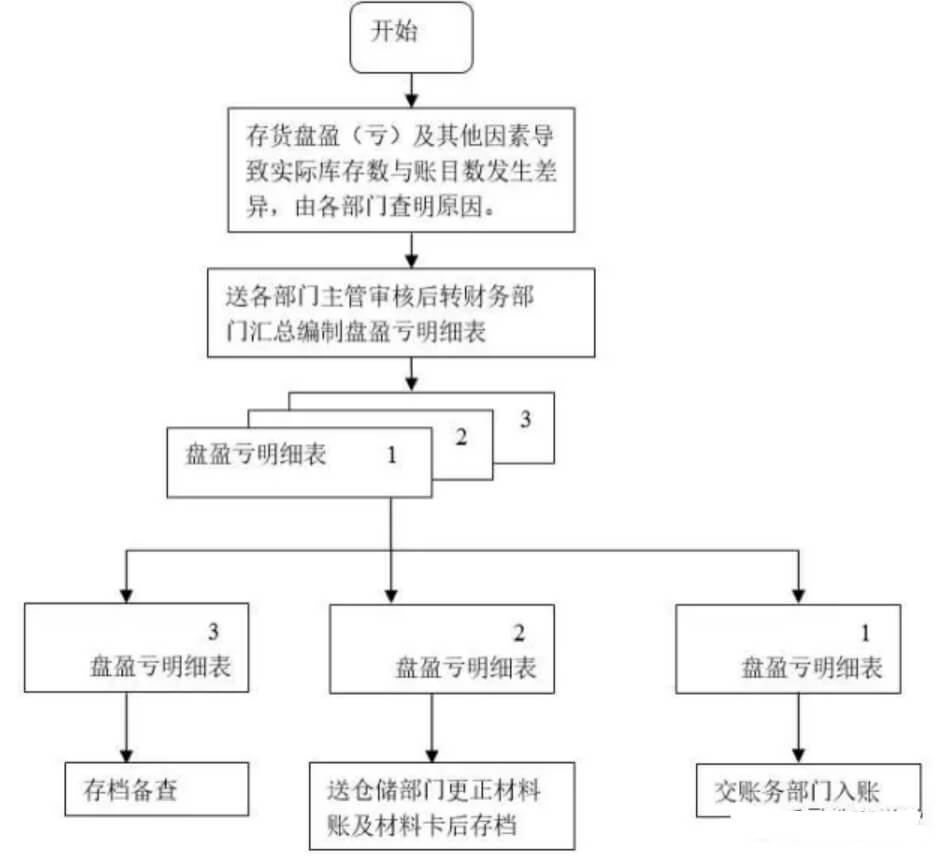
19. How to adjust inventory?
(1) This item is applicable to adjustments when inventory profit (loss) and other factors cause differences between the actual inventory number and the account number.
(2) After each department has identified the reasons for the inventory differences, the financial department will compile an “Inventory Profit (Loss) Detailed Statement”, which should indicate the item number, item name and specifications, account inventory quantity, discrepancy, reasons for adjustments and others. Relevant information is submitted to the department head for signature.
(3) “Inventory Profit and Loss Detailed Statement” in triplicate, distributed by the financial department as follows:
The first page: The financial department records it according to the number and then files it according to the number;
Second copy: Send it to the warehousing department to correct the material account and material card and then file it according to the number.
The third copy: filed by the applying department for future reference.
20. Inventory adjustment operation flow chart
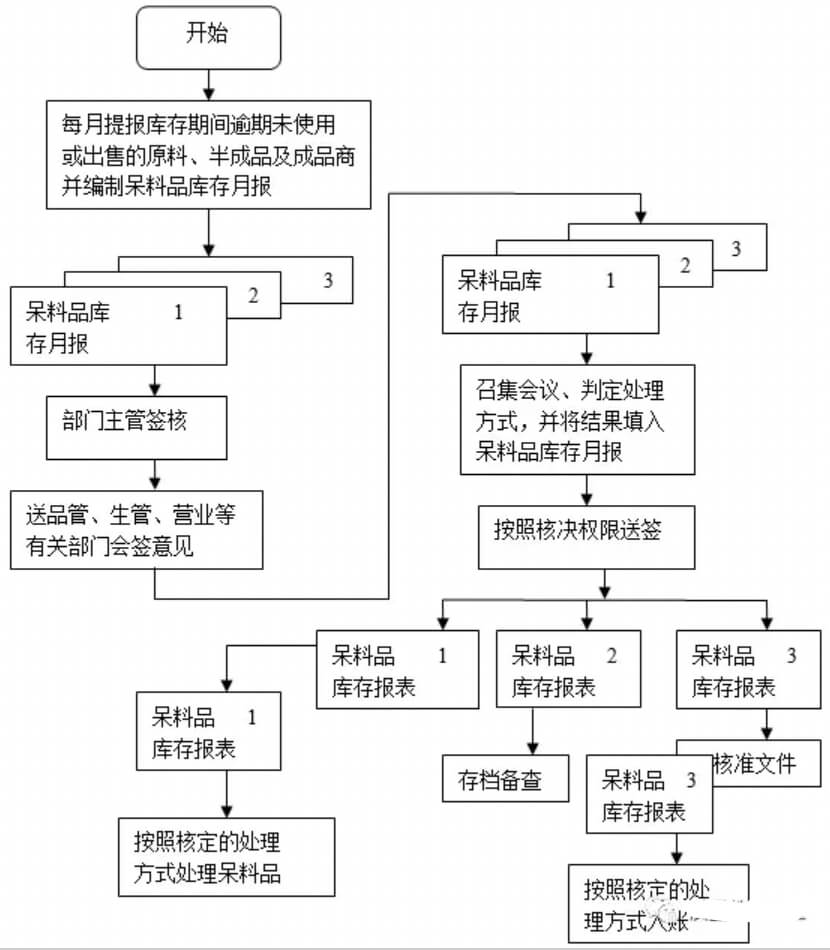
21. How to deal with sluggish materials?
(1) This project is applicable to the processing procedures for sluggish materials that are overdue or unused during the inventory period.
(2) The warehousing department reports every six months the materials that are overdue or unused during the inventory period and prepares a “Dead Material Inventory Report”, indicating the date, material number, product name and specifications, department, existing inventory and other information, and submits it to the department supervisor After approval, quality control, production control, sales and other relevant departments will counter-sign their opinions on the proposed handling method and submit them to the department head.
(3) When the department head receives the “Dead Material Inventory Report”, he should immediately convene relevant department personnel to discuss how to deal with the dead material, fill in the proposed treatment method in the “Dead Material Inventory Report”, and submit a signature according to the authority to decide the treatment method.
(4) The “Dead Material Inventory Report” is in duplicate. After approval, it will be distributed as follows:
The first page: The warehousing department handles dead materials according to the approved handling method;
Second page: The financial department records the accounts in accordance with the approved processing method.
22. Flow chart of waste material adjustment operation
23. Commonly used forms for warehouse operations
(1) Material inventory card
(2) Return sheet
(3) Defective product processing sheet
(4) Material picking list
(5) Production receipt order
(6) Inventory counting
(7) Details of profit (loss)